According to Science, anything that occupies space and has mass is known as matter. Before knowing how many states of matter are there around us, here is a brief into to what matter is. The matter is particles around us that are made up of atoms, i.e., Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, etc. These atoms that we see around us form molecules, which in turn result in the formation of matter. The main energy that holds these atoms and molecules together is called chemical energy. There are almost five states of matter that we witness in our day-to-day life. Here’s a small guide on all that you should know about the states of matter.
Also read:-
How to Draw a Lewis Dot Structure | A Complete Guide
5 States or Phases of Matter
The main five states of matter that you must know include states such as Solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate. Here is a brief overview of the five states of matter present around us.
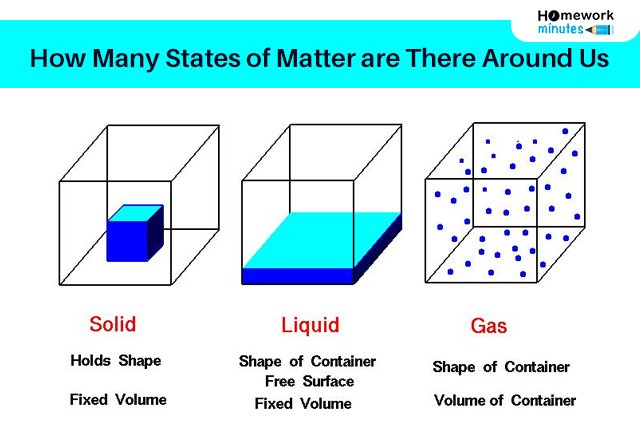
1. Solid
- Particles are packed together in a closed network
- Solid particles have low kinetic energy and high density
- Solids have a strong intermolecular force
- Solids gave high melting points
- The diffusion process of solid-state from one to another is a very slow process.
- Types of Solids are:
a. Crystal Lattice
Crystals are solids with a three-dimensional pattern. This state of matter consists of a particular pattern of atoms or a group of atoms in a symmetrical arrangement placed at regular intervals. The replacement of each group of atoms with a representative point results in the formation of a crystal lattice. The formation of this state of matter is such that it forms a transitional symmetry.
b. Network Covalent Solids
Network covalent solids are state of matter with a giant shape like that of a diamond or graphite. This state of matter has a high melting point, is hard in texture, and is mostly 3-dimensional. Covalent solids are a bad conductor of electricity.
c. Ionic Solids
Ionic solids are solid state of matter with oppositely charged ions. The network of ionic solids is made with both positively and negatively charged anions. When ionic solids dissolve in water, they tend to provide cations and anions that move freely in the water, thus conducting electrical current.
d. Unit Cell
A unit cell is the least complex state of solid matter consuming a definite volume. When the network of these cells repeats themselves, a solid arrangement forms called a lattice.
2. Liquid
- This state of matter carries liquid particles with the capacity to move around each other
- Particles are able to move in a short space
- The liquid state of matter undergoes processes like:
a. Cohesion and Adhesion
This tendency brings the same kind of particles together through the attraction. The cohesive force is present below the liquid surface in high force that attracts the particles from all sides together. As per the U.S. geological survey, water is the most nonmetallic liquid. This tendency of the liquid state of matter accounts for the formation of spheres that occupies the least surface area.
Adhesion is the force of attraction that exists between the two different types of particles. For instance, the water molecules get attracted to the glass molecules.
b. Viscosity
Viscosity is the process by which a liquid state of matter resists free flow. The higher the viscosity, the thicker the liquid, which in turn tends to flow slowly or not at all. For example, in a mixture of water and honey, the latter is more viscous than the former, so it flows slower than the other.
c. Evaporation
Evaporation is the process that the liquid state of matter undergoes constant collision with each other. In this process, the energy transfers from one particle to the other. As the energy transforms the particles, they overcome the surface tension and comes to the surface and evaporates in the air. The liquid particles escaping the surface attain kinetic energy.
d. Volatility
Volatility is the process that finds how likely a liquid molecule is ready to escape or vaporize at normal temperatures. Highly volatile solids tend to sublime at room temperature faster. In this process, a substance passes directly from the solid-state to the gaseous state of matter by skipping the liquid one. The pressure exerted in the closed equilibrium to help substance vaporize called vapor pressure.
3. Gaseous
This state of matter possesses neither a definite shape nor a definite volume. The weak intermolecular space between them provides them free movement in the available space between them. The main properties of the gaseous state of matter are
a. Compressibility
To overcome the weak intermolecular space, the compressibility of the molecules is increased. In this, the temperature decreases and the volume decreases, which in turn lessens the amount of energy that prevents mobilization of the gas molecules. The higher intermolecular pull, in turn, holds the particles together.
b. Expansibility
When the pressure is freed from the gas molecules, the gas that had compressed, gain the ability to expand. The gaseous molecules gain energy to travel far from each other.
c. Diffusibility
The diffusibility of the gas molecules refers to its motion due to high velocity. In this process, two gases get mixed up to help one gas molecule to pass through the other one, thus helping the molecules to get well-diffused. This results in the formation of a homogeneous mixture of gases.
d. Low density
The low density of the gaseous molecules is due to the larger intermolecular spaces and volume.
The exertion of pressure
- Gas particles have the capacity to move in a range of distance.
- Gaseous particles have high kinetic energy and low density.
E.g., Perfumes
e. Plasma
Plasma is a component of the universe with quite high kinetic energy.
These are highly charged particles with superheated energy.
Bose-Einstein Condensate
This state of matter is made due to the combination of the lasers and magnets.
Due to the absence of kinetic energy, the atoms begin to clump up and form a “Super Atom.”